Foreword
News websites and market analysis companies usually do their “trends to watch this year” article in January. It’s said to help digest the turkey and resell useless X-mas presents. As Point The Power doesn’t do anything like the others, here is our “PV market trends of the year” article in September.
Introduction
Solar inverter market has always been very lively. It has grown on the basis of government subsidies and feed-in-tariffs. I agree this was necessary to launch the business. It helped cut-off the chicken and egg problem. And it’s kind of fair that our own money pays, one way or another, to build a business that’s sustainable for the planet while keeping us in our comfort.
Meanwhile, this PV business special treatment was not meant to last forever. As government decreased their help to leave the market roll by itself, rationalization came back. It was required to be more efficient, not about energy produced, but about PV inverter and PV module company’s operation. This shakes-down the market and help consolidate. We now get to a point where we will see a bit more stability.
But what to expect next.
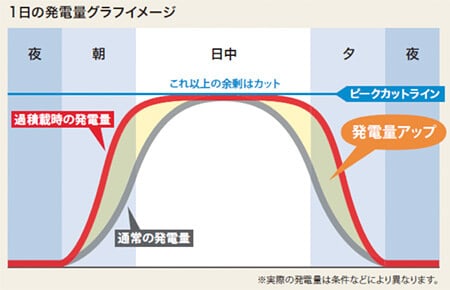
1.500V DC input for solar farm inverter and no less!
This is the main technical trend coming and it’s strongly confirmed. Solar farm installers want higher input voltage: and 1.5kV is the most efficient one. It does not require special high voltage certification and training for installation staff, but it’s still the most efficient combination to build large multiple string installations.
Studies proved it was the best trade-off. So expect every large PV inverter manufacturer to have more and more 1500V DC input power electronics systems in their catalog very soon.
And if you are a protection or combiner box system maker I hope you are aware of that trend and ready to follow.
(Multi-)String inverter at all stages
It’s not because there is a main trend in the utility scale photovoltaic inverter field that the string inverter will stay at residential level. With prices coming down, reliability and monitoring being improved, less than 50kW string and multi-string inverters are still and will keep being used in larger installations. They will also grow in size, and you will more powerful multi-string inverter in the future.
Merger & Acquisition: A summary
The last 3 years have been very active. A lot of companies decided to leave the PV business, sell their assets, and a few others took the opportunity to expand or enter new geographical markets.
As a picture is always more than a thousand words, take a look at our analysis here under:
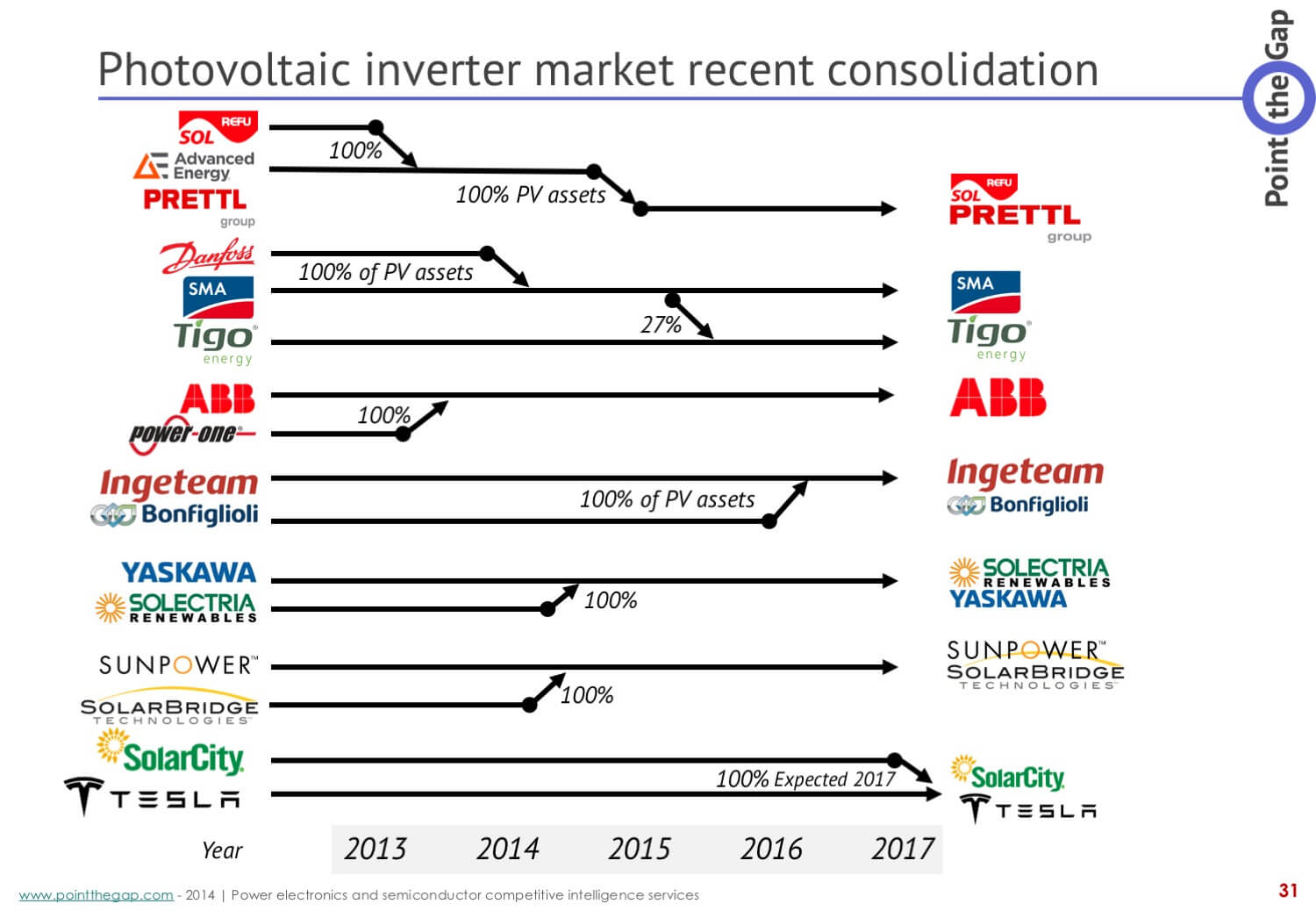
Integration is the leitmotiv
There has been a lot of innovation and predictions about innovation. We now feel like there is a renew, all for the best of the photovoltaic world. Tesla recently announced they are working on how to build a solar roof. They did not mean how to put solar on a roof that is already here, or integrate solar on a roof, but build a roof that produces electricity. That’s quite new in the fact that it’s targeting an unexploited market so far: People who want to renovate the roof of their house. These people could not install PV before renovation, and might not have to pay for both a roof, and then a PV installation. If both are done at the same time, the equation is changed. We believe that’s what Elon Musk see has his plan for SolarCity.
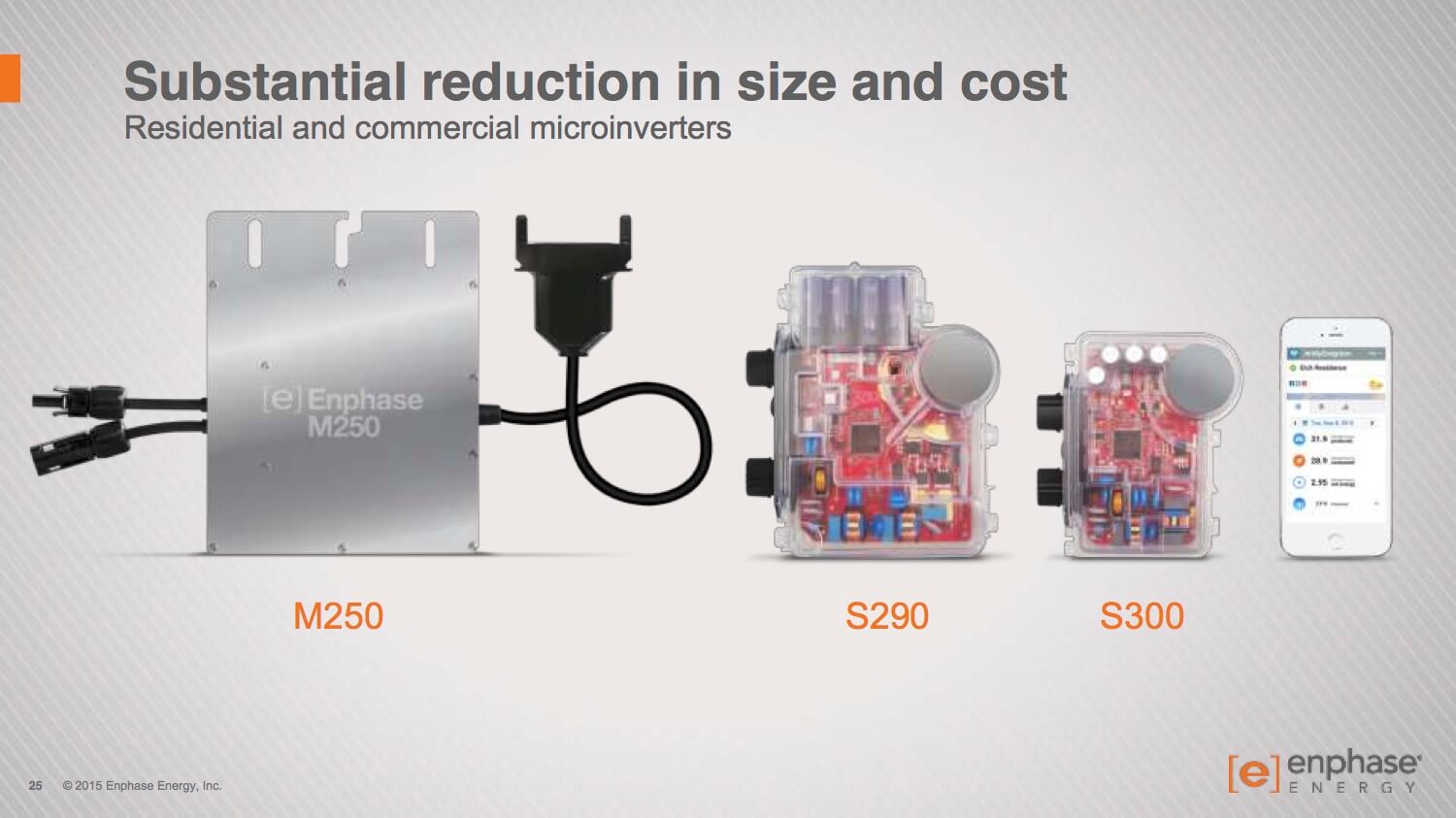
Enphase integration power electronics size reduction photovoltaic mi
Micro inverter world is changing too. If you follow our blog, you have seen a lot of innovations in topology and use of GaN devices for Consumer and smartphone laptop chargers. These converters are a bit smaller than Microinverters but still use the same type of components (Super Junction MOSFET today, GaN Transistors tomorrow). Enphase recently confirmed that they are redesigning their product line with more integration, with faster switching for power devices and a proprietary control IC. We should see a cost reduction resulting from these innovations. This comes right when the Module Level Power Electronics (MPLE) segment is revitalized.